Basic Package Management
RPM (Redhat Package Manager)
- Specially formatted File(s) packaged together with the .rpm extension.
- Packages included or available for RHEL are in rpm format.
- Metadata info gets updated whenever a package is updated.
rpm command
- Install, Upgrade, remove, query, freshen, or decompress packages.
- Validate package authenticity and integrity.
Packages
- Two types of packages binary (or installable) and source.
Binary packages
- Installation ready
- Bundled for distribution.
- Have .rpm extension.
- Contain:
- install scripts (pre and post)
- Executables
- Configuration files
- Library files
- Dependency information
- Where to install files
- Documentation
- How to install/uninstall
- Man pages for config files/commands
- Other install and usage info
- Metadata
- Stored in central location
- Includes:
- Package version
- Install location
- Checksum values
- List of included files and their attributes
- Package intelligence
- Used by package administration toolset for successful completion of the package installation process.
- May include info on:
- prerequisites
- User account setup
- Needed directories/ soft links
- Includes reverse process for uninstall
Package Naming
5 parts to a package name: 1. Name 2. Version 3. release (revision or build) 4. Linux version 5. Processor Architecture - noarch - platform independant - src - Source code packages
- Always has .rpm extension
- .rpm is removed after install Example: openssl-1.1.1-8.el8.x86_64.rpm,
Package Dependency
- Dependency info is in the metadata
- Read by package handling utilities
Package Database
- Metadata for installed packages and package files is stored in /var/lib/rpm/
- Package database
- Referenced by package manipulation utilities to obtain:
- package name and version data
- Info about owerships, permissions, timestamps, and file sizes that are part of the package.
- Contain info on dependencies.
- Aids management commands in:
- listing and querying packages
- Verifying dependencies and file attributes.
- Installing new packages.
- Upgrading and uninstalling packages.
- Removes and replaces metadata when a package is replaced.
- Can maintain multiple version of a single package.
Package Management Tools
- rpm (redhat package manager)
- Does not automatically resolve dependencies.
- yum (yellowdog update, modified)
- Find, get, and install dependencies automatically.
- softlink to dnf now.
- dnf (dandified yum)
Package management with rpm
rpm package management tasks: - query - install - upgrade - freshen - overwrite - remove - extract - validate - verify
- Works with installed and installable packages.
rpm command
Query options
Query and display packages
-q (--query)
List all installed packages
-qa (--query --all)
List config files in a package
-qc (--query --config-files)
List documentation files in a package
-qd (--query --docfiles)
Exhibit what package a file comes from
-qf (--query --file)
Show installed package info (Version, Size, Installation status, Date, Signature, Description, etc.)
-qi (--query --info)
Show installable package info (Version, Size, Installation status, Date, Signature, Description, etc.)
-qip (--query --info --package)
List all files in a package.
-ql (--query --list)
List files and packages a package depends on.
-qR (--query --requires)
List packages that provide the specified package or file.
-q --whatprovides
List packages that require the specified package or file.
-q --whatrequires
Package installation options
Remove a package
-e (--erase)
Upgrades installed package. Or loads if not installed.
-U (--upgrade)
Display detailed information
-v (--verbose or -vv)
Verify integrity of a package or package files
-V (--verify)
Querying packages
Query packages in the package database or at a specified location.
Installing a package
- Creates directory structure needed
- Installs files
- Runs needed post installation steps
- Installing package will fail if missing dependencies.
- Error message will show missing dependencies.
Upgrading a package
- Installs the package if previous version does not exist. (-U)
- Makes backup of effected configuration files and adds .rpmsave extension.
Freshening a package
- Older version must exist.
- -F option
- Will only work if a newer version of a package is available.
Overwriting a Package
- Replaces existing files of a package with the same version.
- –replacepkgs option.
- Useful when you suspect corruption.
Removing a Package
- Uninstalls package and associated files/ directories
- -e Option
- Checks to see if this package is a dependency for another program and fails if it is.
Extracting Files from an Installable Package
rpm2cpiocommand- -i (extract)
- -d create directory structure.
Useful for:
- Examining package contents.
- Replacing corrupt or lost command.
- Replace critical configuration file to it’s original state
Package Integrity and Credibility
- MD5 Checksum for verifying package integrity
- GNU Privacy Guard Public Key (GNU Privacy Guard or GPG) for ensuring credibility of publisher.
- PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) - commercial version of GPG.
--nosignature- Don’t verify package or header signatures when reading.
-K- keep package files after installation
rpmkeyscommand - check credibility, import GPG key, and verify packages
- keep package files after installation
- Redhat signs their products and updates with a GPG key.
- Files in installation media include public keys in the products for verification.
- Copied to /etc/pki/rpm-gpg during OS installation.
RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release
- Used for packages shipped after November 2009 and their updates. RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-beta
- For Beta products shipped after November 2009.
- Import the relevant GPG key and the verify the package to check the credibility of a package.
Viewing GPG Keys
- view with rpm command
rpm -q gpg-pubkey -ioption- show info about a key.
Verifying Package Attributes
- Compare package file attributes with originals stored in package database at the time of installation.
-Voption- compare owner, group, permission mode, size, modification time, digest, type, etc.
- Returns to prompt if no changes are detected
- -v or vv for verbose
-Vf- run the check directly on the file
- Three columns of output:
- Column 1
- 9 fields
- S = Different file size.
- M = Mode or permission or file type change.
- 5 = MD5 Checksum does not match.
- D = Device file and its major and minor number have changed.
- L = File is a symlink and it’s path has been altered.
- U = Ownership has changed.
- G = Group membership has been modified.
- T = Timestamp changed.
- P = Capabilities are altered.
- . = No modifications detected.
- 9 fields
- Column 2
- File type
- c = Configuration file
- d = Documentation File
- g = Ghost FIle
- l = License file
- r = Readme file
- File type
- Column 3
- Full path of file
- Column 1
Basic Package Management Labs
Lab: Mount RHEL 9 ISO Persistently
-
Go to the VirtualBox VM Manager and make sure that the RHEL 8 image is attached to RHEL9-VM1 as depicted below:
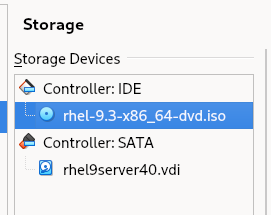

-
Open the /etc/fstab file in the vim editor (or another editor of your choice) and add the following line entry at the end of the file to mount the DVD image (/dev/sr0) in read-only (ro) mode on the /mnt directory.
/dev/sr0 /mnt iso9660 ro 0 0
Note: sr0 represents the first instance of the optical device and iso9660 is the standard format for optical file systems.
-
Mount the file system as per the configuration defined in the /etc/fstab file using the mount command with the -a (all) option:
sudo mount -a -
Verify the mount using the df command:
df -h | grep mnt
Note: The image and the packages therein can now be accessed via the /mnt directory just like any other local directory on the system.
-
List the two directories—/mnt/BaseOS/Packages and /mnt/AppStream/Packages—that contain all the software packages (directory names are case sensitive):
ls -l /mnt/BaseOS/Packages | more
Lab: Query Packages (RPM)
-
query all installed packages:
rpm -qa -
query whether the perl package is installed:
rpm -q perl -
list all files in a package:
rpm -ql iproute -
list only the documentation files in a package:
rpm -qd audit -
list only the configuration files in a package:
rpm -qc cups -
identify which package owns the specified file:
rpm -qf /etc/passwd -
display information about an installed package including version, release, installation status, installation date, size, signatures, description, and so on:
rpm -qi setup -
list all file and package dependencies for a given package:
rpm -qR chrony -
query an installable package for metadata information (version, release, architecture, description, size, signatures, etc.):
rpm -qip /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/zsh-5.5.1-6.el8.x86_64.rpm -
determine what packages require the specified package in order to operate properly:
rpm -q --whatrequires lvm2
Lab: Installing a Package (RPM)
- Install zsh-5.5.1-6.el8.x86_64.rpm
sudo rpm -ivh /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/zsh-5.5.1-6.el8.x86_64.rpm
Lab: Upgrading a Package (RPM)
- Upgrade sushi with the -U option:
sudo rpm -Uvh /mnt/AppStream/Packages/sushi-3.28.3-1.el8.x86_64.rpm
Lab: Freshening a Package
- Freshen the sushi package:
sudo rpm -Fvh /mnt/AppStream/Packages/sushi-3.28.3-1.el8.x86_64.rpm
Lab: Overwriting a Package
- Overwrite zsh-5.5.1-6.el8.x86_64
sudo rpm -ivh --replacepkgs /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/zsh-5.5.1-6.el8.x86_64
Lab: Removing a Package
- Remove sushi
sudo rpm sushi -ve
Lab: Extracting Files from an Installable Package
-
You have lost /etc/crony.conf. Determine what package this file comes from:
rpm -qf /etc/chrony.conf -
Extract all files from the crony package to /tmp and create the directory structure:
[root@server30 mnt]# cd /tmp
[sudo rpm2cpio /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/chrony-3.3-3.el8.x86_64.rpm | cpio -imd
1066 blocks](<[root@server30 tmp]# rpm2cpio /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/chrony-4.3-1.el9.x86_64.rpm | cpio -imd
1253 blocks>)-
Use find to locate the crony.conf file:
sudo find . -name chrony.conf -
Copy the file to /etc:
Lab: Validating Package Integrity and Credibility
- Check the integrity of zsh-5.5.1-6.el8.x86_64.rpm located in /mnt/BaseOS/Packages:
rpm -K /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/zsh-5.5.1-6.el8.x86_64.rpm --nosignature - Import the GPG key from the proper file and verify the signature for the zsh-5.5.1-6.el8.x86_64.rpm package.
sudo rpmkeys --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-redhat-release
sudo rpmkeys -K /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/zsh-5.5.1-6.el8.x86_64.rpmLab: Viewing GPG Keys
- List the imported key:
rpm -q gpg-pubkey - View details for the first key:
rpm -qi gpg-pubkey-fd431d51-4ae0493b
Lab: Verifying Package Attributes
-
Run a check on the at program:
sudo rpm -V at -
Change permissions of one of the files and run the check again:
ls -l /etc/sysconfig/atd
sudo chmod -v 770 /etc/sysconfig/atd
sudo rpm -V at-
Run the check directly on the file:
sudo rpm -Vf /etc/sysconfig/atd -
Reset the value and check the file again:
sudo chmod -v 644 /etc/sysconfig/atd
sudo rpm -V atLab: Perform Package Management Using rpm
- Run the
lscommand on the /mnt/AppStream/Packages directory to confirm that the rmt package is available:
[root@server30 tmp]# ls -l /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/rmt*
-r--r--r--. 1 root root 49582 Nov 20 2021 /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/rmt-1.6-6.el9.x86_64.rpm- Run the rpm command and verify the integrity and credibility of the package:
[root@server30 tmp]# rpmkeys -K /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/rmt-1.6-6.el9.x86_64.rpm
/mnt/BaseOS/Packages/rmt-1.6-6.el9.x86_64.rpm: digests signatures OK- Install the Package:
[root@server30 tmp]# rpmkeys -K /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/rmt-1.6-6.el9.x86_64.rpm
/mnt/BaseOS/Packages/rmt-1.6-6.el9.x86_64.rpm: digests signatures OK
[root@server30 tmp]# rpm -ivh /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/rmt-1.6-6.el9.x86_64.rpm
Verifying... ################################# [100%])
Preparing... ################################# [100%])
Updating / installing...
1:rmt-2:1.6-6.el9 ################################# [100%])- Show basic information about the package:
[root@server30 tmp]# rpm -qi rmt
Name : rmt
Epoch : 2
Version : 1.6
Release : 6.el9
Architecture: x86_64
Install Date: Sat 13 Jul 2024 09:02:08 PM MST
Group : Unspecified
Size : 88810
License : CDDL
Signature : RSA/SHA256, Sat 20 Nov 2021 08:46:44 AM MST, Key ID 199e2f91fd431d51
Source RPM : star-1.6-6.el9.src.rpm
Build Date : Tue 10 Aug 2021 03:13:47 PM MST
Build Host : x86-vm-55.build.eng.bos.redhat.com
Packager : Red Hat, Inc. <http://bugzilla.redhat.com/bugzilla>
Vendor : Red Hat, Inc.
URL : http://freecode.com/projects/star
Summary : Provides certain programs with access to remote tape devices
Description :
The rmt utility provides remote access to tape devices for programs
like dump (a filesystem backup program), restore (a program for
restoring files from a backup), and tar (an archiving program).- Show all the files the package contains:
[root@server30 tmp]# rpm -ql rmt
/etc/default/rmt
/etc/rmt
/usr/lib/.build-id
/usr/lib/.build-id/c2
/usr/lib/.build-id/c2/6a51ea96fc4b4367afe7d44d16f1405c3c7ec9
/usr/sbin/rmt
/usr/share/doc/star
/usr/share/doc/star/CDDL.Schily.txt
/usr/share/doc/star/COPYING
/usr/share/man/man1/rmt.1.gz- List the documentation files the package has:
[root@server30 tmp]# rpm -qd rmt
/usr/share/doc/star/CDDL.Schily.txt
/usr/share/doc/star/COPYING
/usr/share/man/man1/rmt.1.gz- Verify the attributes of each file in the package. Use verbose mode.
[root@server30 tmp]# rpm -vV rmt
......... c /etc/default/rmt
......... /etc/rmt
......... a /usr/lib/.build-id
......... a /usr/lib/.build-id/c2
......... a /usr/lib/.build-id/c2/6a51ea96fc4b4367afe7d44d16f1405c3c7ec9
......... /usr/sbin/rmt
......... /usr/share/doc/star
......... d /usr/share/doc/star/CDDL.Schily.txt
......... d /usr/share/doc/star/COPYING
......... d /usr/share/man/man1/rmt.1.gz- Remove the package:
[root@server30 tmp]# rpm -ve rmt
Preparing packages...
rmt-2:1.6-6.el9.x86_64Lab 9-1: Install and Verify Packages
As user1 with sudo on server3,
- make sure the RHEL 9 ISO image is attached to the VM and mounted.
- Use the rpm command and install the zsh package by specifying its full path.
[root@server30 Packages]# rpm -ivh /mnt/BaseOS/Packages/zsh-5.8-9.el9.x86_64.rpm
Verifying... ################################# [100%])
Preparing... ################################# [100%])
package zsh-5.8-9.el9.x86_64 is already installed- Run the rpm command again and perform the following on the zsh package:
- (1) show information
[root@server30 Packages]# rpm -qi zsh
Name : zsh
Version : 5.8
Release : 9.el9
Architecture: x86_64
Install Date: Sat 13 Jul 2024 06:49:40 PM MST
Group : Unspecified
Size : 8018363
License : MIT
Signature : RSA/SHA256, Thu 24 Feb 2022 08:59:15 AM MST, Key ID 199e2f91fd431d51
Source RPM : zsh-5.8-9.el9.src.rpm
Build Date : Wed 23 Feb 2022 07:10:14 AM MST
Build Host : x86-vm-56.build.eng.bos.redhat.com
Packager : Red Hat, Inc. <http://bugzilla.redhat.com/bugzilla>
Vendor : Red Hat, Inc.
URL : http://zsh.sourceforge.net/
Summary : Powerful interactive shell
Description :
The zsh shell is a command interpreter usable as an interactive login
shell and as a shell script command processor. Zsh resembles the ksh
shell (the Korn shell), but includes many enhancements. Zsh supports
command line editing, built-in spelling correction, programmable
command completion, shell functions (with autoloading), a history
mechanism, and more.- (2) validate integrity
[root@server30 Packages]# rpm -K zsh-5.8-9.el9.x86_64.rpm
zsh-5.8-9.el9.x86_64.rpm: digests signatures OK- (3) display attributes
[root@server30 Packages]# rpm -V zsh
Lab 9-2: Query and Erase Packages
As user1 with sudo on server3,
- make sure the RHEL 9 ISO image is attached to the VM and mounted.
- Use the rpm command to perform the following:
- (1) check whether the setup package is installed
[root@server30 Packages]# rpm -q setup
setup-2.13.7-10.el9.noarch- (2) display the list of configuration files in the setup package
[root@server30 Packages]# rpm -qc setup
/etc/aliases
/etc/bashrc
/etc/csh.cshrc
/etc/csh.login
/etc/environment
/etc/ethertypes
/etc/exports
/etc/filesystems
/etc/fstab
/etc/group
/etc/gshadow
/etc/host.conf
/etc/hosts
/etc/inputrc
/etc/motd
/etc/networks
/etc/passwd
/etc/printcap
/etc/profile
/etc/profile.d/csh.local
/etc/profile.d/sh.local
/etc/protocols
/etc/services
/etc/shadow
/etc/shells
/etc/subgid
/etc/subuid
/run/motd
/usr/lib/motd- (3) show information for the zlib-devel package on the ISO image
[root@server30 Packages]# rpm -qi ./zlib-devel-1.2.11-40.el9.x86_64.rpm
Name : zlib-devel
Version : 1.2.11
Release : 40.el9
Architecture: x86_64
Install Date: (not installed)
Group : Unspecified
Size : 141092
License : zlib and Boost
Signature : RSA/SHA256, Tue 09 May 2023 05:31:02 AM MST, Key ID 199e2f91fd431d51
Source RPM : zlib-1.2.11-40.el9.src.rpm
Build Date : Tue 09 May 2023 03:51:20 AM MST
Build Host : x86-64-03.build.eng.rdu2.redhat.com
Packager : Red Hat, Inc. <http://bugzilla.redhat.com/bugzilla>
Vendor : Red Hat, Inc.
URL : https://www.zlib.net/
Summary : Header files and libraries for Zlib development
Description :
The zlib-devel package contains the header files and libraries needed
to develop programs that use the zlib compression and decompression
library.- (4) reinstall the zsh package (–reinstall -vh),
[root@server30 Packages]# rpm -hv --reinstall ./zsh-5.8-9.el9.x86_64.rpm
Verifying... ################################# [100%])
Preparing... ################################# [100%])
Updating / installing...
1:zsh-5.8-9.el9 ################################# [ 50%])
Cleaning up / removing...
2:zsh-5.8-9.el9 ################################# [100%])- (5) remove the zsh package.
[root@server30 Packages]# rpm -e zsh